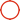
The working principle of an electric actuator can be simply understood as follows: It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to drive valves or equipment, enabling automated control.
An electric actuator typically consists of a motor, reduction mechanism, transmission device, position feedback system, and control circuit. When the control system issues a command,
the motor starts: converting electrical energy into mechanical energy.
The reduction mechanism: reduces the high-speed rotation of the motor to a suitable low-speed, high-torque output.
The transmission device: transfers the output torque to the valve stem or equipment, enabling actions such as valve opening/closing or damper adjustment.
Position feedback: Sensors such as potentiometers, encoders, or Hall elements transmit the valve position signal back to the control system, achieving closed-loop control.
- High precision
- High degree of automation
- Strong driving force
- High reliability
- In petrochemical production lines, electric actuators drive butterfly valves to precisely regulate medium flow.
- In building HVAC systems, electric actuators control the opening of air dampers to adjust air conditioning airflow.
- In power plants, actuators work in conjunction with boiler systems to regulate steam flow and improve energy utilization efficiency.